Key Takeaways:
- A Master’s in Psychology opens up various career opportunities beyond clinical and counseling roles, including fields like organizational psychology and research.
- Graduates with a Master’s in Psychology can also pursue non-traditional paths such as roles in human resources, market research, and educational psychology, where they can apply psychological principles in diverse settings.
- Additional certification or licensure might be required for certain positions, such as a therapist or counselor, depending on the state and the specific job requirements.
With a Master’s in Psychology, there are many career paths, and you can work with individuals or entire populations. This field involves studying the human mind to understand human behavior. Many enter college to earn an undergraduate degree in psychology. And they plan to return to school at least once throughout their careers.
Earning a bachelor’s degree in psychology enables graduates to work in entry-level positions. Additionally, psychology majors can then find a concentration that suits them best. There are both online and traditional programs for undergraduate psych degrees. A bachelor’s degree holders with a psychology major can enter the workforce on a career path or choose a degree path to pursue a more advanced degree (doctoral programs). With a master’s degree in psychology graduates can find teaching or contributing writer jobs in psychology programs at community colleges, work at law firms, go into human resources, or work in data analysis. Again, they can also prepare for a doctoral degree college program.
Why Earn a Master’s in Psychology?
A master’s degree in psychology helps students refine their knowledge of an area of interest and find better employment and career options. So, is a master’s in psychology worth it? Yes. Getting a master’s in psychology can lead to earning a PhD and accessing many rewarding jobs. What Can You Do With a Master’s in Psychology?
Completing an undergraduate degree in psychology is just the first step toward a career. With a few additional requirements, there are many career paths. You’ll need to earn your master’s degree to find meaningful employment in the concentration of your choice (according to labor statistics). This graduate degree can be a Master of Arts (MA) or a Master of Science (MS). So, what can I do with a MA in Psychology?
How to Choose a Master’s Program
There are many things to consider when looking for a master’s program. Some are the convenience of the coursework and classes, quality of education, accreditation, and the degree’s value in finding employment in a particular concentration.
Other factors to consider may be joining professional associations. These groups help individuals discover resources, stay informed about changes in the field, enhance knowledge, and access support when needed.
Psychology offers many opportunities to lead rewarding careers for those who want to understand the human mind to help society. However, if it is unsuitable for you, but you enjoy helping people, consider other fields. Some similar degrees are a Masters in Healthcare Administration (MHA) degree or a Masters in Social Work (MSW) degree. Many Social Workers also counsel in clinical settings. Other popular careers include Anthropology, Human Resources, Leadership Management, Consulting, Recruiting, and Marketing.
School Accreditation for Master’s in Psychology Degrees
Accreditation is an essential credential for a psych degree program. It ensures that the standard of education you receive is acceptable to employers, the government, licensing bodies, and the public. A majority of reputable schools have regional or national accreditation. It is essential to attend an accredited school so you can receive financial aid. Additionally, an accredited degree can help you find employment because it is recognized by future employers.
Regional Accreditation for Schools
Accreditation for master’s degree programs typically falls under regional accreditation. There are six regional accrediting institutions for master in psychology programs.
- Middle States Commission on Higher Education
- New England Association of Schools and Colleges
- North Central Association Commission on Accreditation
- Northwest Commission on Higher Education
- Southern Association of Schools and Colleges
- Western Association of Schools and Colleges
Program Accreditation
Accreditation for an online master’s in psychology is equally important. Look through the curriculum information on the school’s website to find the accreditation information for the program. If you’re unsure about the accreditation, you can search the US Department of Education’s Database of Accredited Postsecondary Institutions and Programs (OPE).
American Psychological Association (APA)
The APA is the most well-known accrediting body for psychology programs. But it only provides accreditation for doctoral programs, doctoral internships, and postdoctoral residencies. If you continue pursuing your education through the doctorate level, you should attend an advanced degree program with APA accreditation.
Masters in Psychology and Counseling Accreditation Council (MPCAC)
The MPCAC is another organization that provides accreditation for masters in psychology programs. It provides additional accreditation to psychology master’s degree programs in regionally accredited colleges and universities in the US. The MPCAC is approved by the Council for Higher Edu (CHEA).
Commission on Accreditation for Marriage and Family Therapy Education (COAMFTE)
The COAMFTE also provides accreditation. This group accredits master’s programs focusing on marriage and therapy.
Many of these organizations provide accreditation for master’s in psychology online. You can also check for regional accreditation or accreditation from another organization recognized by the Department of Education or the Council for Higher Edu.
Types of Psychology Master’s Degrees
Psychology is wide and varied in the areas of specialization available to graduate students. It is used in business, economics, industrial and manufacturing, public health, criminology, health sciences, and more. Most programs at the undergraduate level prepare bachelor’s degree holders for the basics of working in the field in various industries. They also prepare students to continue on to graduate school and earn a graduate degree.
At the same time, the master’s in psychology allows you to focus on an area that you find most appealing. Some master’s in psychology graduate programs and PhDs are terminal degrees and do not require additional education for a rewarding career. Doctoral degrees in psychology offer the most employment opportunities for individuals interested in clinical work with different types of psychological issues.
- 25 Best Psychology Master’s Programs
- 15 Best Online Psychology Master’s Programs
- 10 Fastest Online Psychology Master’s Programs
Below are some of the top concentrations in psychology master’s degree programs.
Counseling Psychology
The counseling concentration is considered a general practice and health service provider role. The role requires a deeper understanding of how people function in their relationships at all life stages. Counseling involves working with an individual to help them with various mental health issues and assist them in a time of crisis. Counseling psychologists who provide counseling also assess and diagnose psychological symptoms, determine their severity, then treat the patient and their symptoms. Career paths for this psychology program include marriage and family therapists.
Social Psychology
Social psychology involves the study of social interactions between groups of people in various physical environments and social settings. This area of psychology aims to better understand how group dynamics influence people’s actions and decisions within themselves and others. The information learned from the study of social groups is used to design and evaluate policies, develop conflict resolution techniques, and also educational programs for academic settings.
Forensic Psychology
The role of a forensic psychologist is one of studying forensic psychology, which is criminal populations and individuals who are incarcerated. Forensic psychology has become popular due to criminal TV shows and movies with a psychologist who creates personality and behavioral profiles of criminals. They work closely with other professionals in the justice system to determine an incarcerated individual’s mental stability. Forensic psychology graduates also create a treatment program and provide recommendations for handling an incarcerated individual.
Clinical Psychology
A Clinical Psychologist work with individuals or groups in multiple sectors. You may find yourself working with people in a health service setting, research, and anywhere there’s a need for someone with clinical psychology training and skills to help people with their mental health needs. Clinical psychologists conduct clinical psychology research and work with diverse populations to understand the challenges they face. One who works in a clinical setting must help their patients understand their issues, how to manage them, and find a path to wellness. Licensed Professional Clinical Counselors (LPCC) can work in family therapy as licensed family therapists. Strong communication skills are a must.
- 25 Best Counseling Bachelor’s Programs
- 15 Best Online Counseling Masters Programs
- 25 Best Counseling Master’s Programs
School Psychology
A school psychologist works in elementary, junior high, and high schools. These professionals are integral in monitoring the mental health of the student body and individual students. They also intervene when an individual needs help and in the school system. The school psychologist also creates and develops programs for positive learning environments, then implements and evaluates them to make changes as needed. School psychology career paths can be rewarding!
Industrial Organizational or I/O Psychology
Industrial-organizational psychologists study and research employee satisfaction, productivity, and consumer behavior. Using their educational background and psychology skills, these professionals work to increase workplace and customer satisfaction to make a business run more efficiently. I/O or Industrial and Organizational Psychology is also one of the fastest growing experimental psychology areas.

Other Psychology Specializations
Below are other options for psychology students to look into. These are areas of concentration, focus, or specialization with a master’s in psychology.
- Mental Health
- Marriage and Family Therapy
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Behavioral and Substance Abuse
- Child Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Psychiatry Research
- Sports Psychology
- Business Psychology (private sectors)
- Industrial Organizational Psychology
- Experimental Psychology
These specializations represent entirely different psychology disciplines. What can you do with a psychology masters? You’ll be able to easily find a concentration that matches your educational goals, and in the area of psychology you want to gain expertise. If you want to return to school and earn your Ph.D. in psychology, ensure that the online master’s of psychology degree leads to a doctorate to quickly transfer your credits. Becoming a psychology professional is always within your reach.
Certifications and Licenses for Master’s in Psychology
Most states do not require licensure for people who earn a master’s in psychology degree. But you may not be able to work directly upon graduation. Currently, no states allow people with a master’s degree in psychology to work independently, but some allow a master’s level psychologist to work in specific settings.
States for Master’s Behavior Anal
Practice with Supervision
Some states allow psychologists with a master’s in psychology to practice under the supervision of a board-certified psychologist.
These states title a master’s psychologist a psychological associate. Most of these states require post-graduate work experience, practicum hours, or a residency from the school you attended to apply for a license. You must sit for the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP) to get licensure as a psychological associate or a psychologist. All states require you to pass the exam before granting you licensure.
States that do not license people with master’s degrees in psychology also do not prevent you from working. Additionally, employers can hire candidates with a master’s degree in psychology and place them in roles that train them as psychologists.
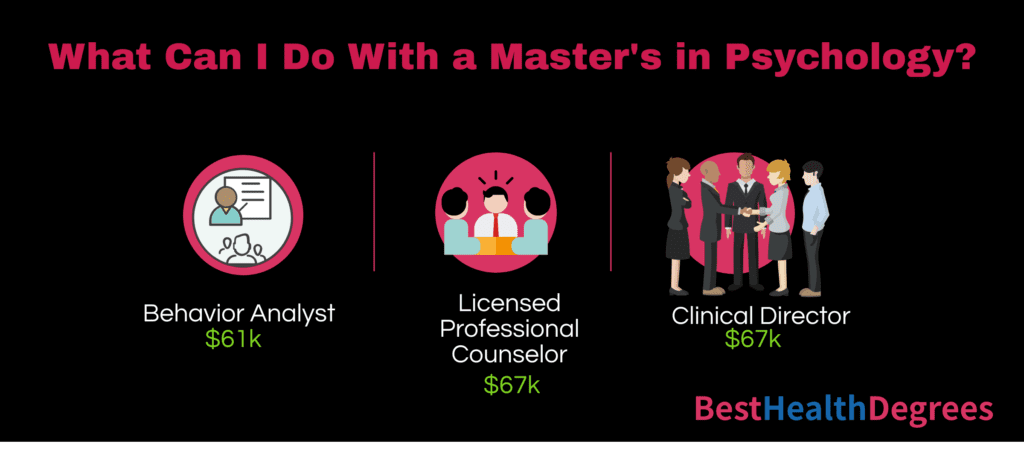
Careers in Psychology
So, what can you do with a master’s degree in Psychology? As previously mentioned, the field offers multiple concentrations and a broad range of specializations underneath its central umbrella. Students who complete master’s programs in psychology can findemployment in every professional field that aligns with a specific concentration in psychology. These professionals work in government agencies, corporate settings, and private sectors.
Master’s degree jobs in psychology are also beneficial for gaining work experience hours. Some students work before returning to school to earn a PhD or take the next steps in another career path. For example, some students may decide to go to Law School and influence public policy.
Many states don’t have a licensing requirement for masters in psychology jobs that allows you to work under the supervision of a licensed psychologist.

Jobs with a Master’s in Psychology
Psychology students have a broad range of places where they can seek employment. Depending on their career goals they can work in psychological research, higher education, or as a licensed therapist. Additionally, many individuals with a doctorate pursue research careers. Below are some of the many job opportunities.
- Adjunct Instructors or Faculty/ Adjunct Faculty at the university level
- School Psychologist / School Psychologists
- Survey Researchers / Research Assistant
- Marriage and Family Therapist / Marriage and Family Therapists
- Industrial-Organizational Psychologist / Industrial-Organizational Psychologists
- Market Research Analyst / Market Research Analysts
- Forensic Psychologist / Forensic Psychologists
- Community Psychologist / Community Psychologists
- Behavioral Health Psychologist /Behavioral Disorder Psychologist
- Training and Development Specialist / Training and Development Specialists
- Human Resources Specialist / Human Resources Specialists
- Sports Psychologist / Sports Psychologists
- Career counselor / Career counselors
- Program Director
- Victim Advocate
- Veteran Psychologist or Counselor
Employers with a Master’s Degree in Psychology
What Can You Do With a Master’s in Psychology? One great job option for a graduate with such a degree is to work in schools. That includes all levels from elementary to university. Master’s degree holders can make much more than others in conventional teaching positions. The federal government is another major employer, but the job titles are not always directly related to psychology.
Instead, the jobs available to a master’s-level psychologist are roles that require an applicant to have a background in psychology to perform their work. Other settings where these professionals work in private practices, hospitals, social services, courts and prisons in the criminal justice system, and community mental health centers. Many employers utilize different aspects of psychology expertise. You can gain experience in a wide variety of areas.
Professionals with a terminal degree may find employment prospects at higher levels, with more competition. Many different organizational settings employ psychologists who have had graduate study. For further study, this article explores doctoral programs.
Average Salary for a Master’s in Psychology
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median salary with a master’s in psychology is $80,040 per year. This amount represents the median pay for people with a graduate degree in psychology. Psychologists with an undergraduate degree major tend to earn less because the field expects people to hold a master’s degree at the very least.
Those with PhDs, or doctorate degrees in psychology, stand to earn the most according to labor statistics. A PhD is expected of most people seeking employment in their chosen subject of study for psychology. So, the average salary for a master’s degree in psychology may be lower than a doctoral degree in psychology.
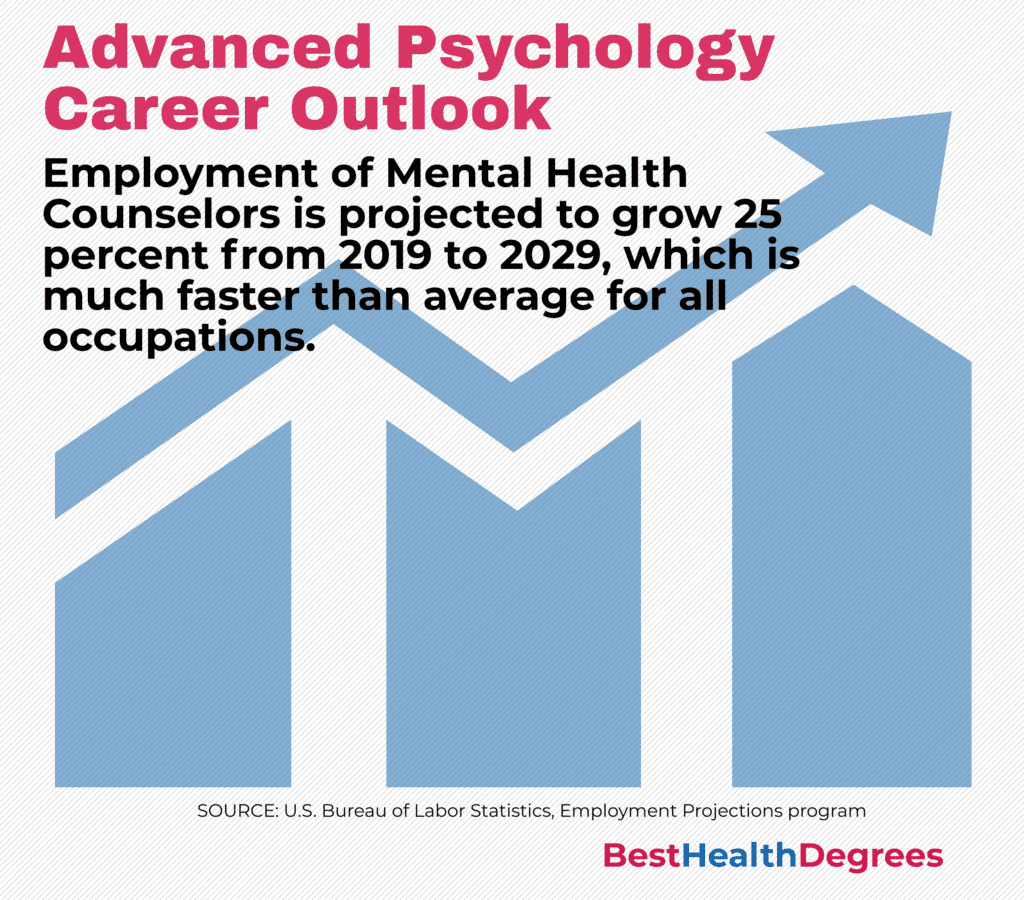
Job Outlook and Growth
The Bureau of Labor Statistics expects future employment in psychology to grow 8% between 2020 and 2030, which is as fast as the average growth in employment for the same period. In 2020, there were 178,900 jobs for individuals who earned a master’s in psychology, and the field is expected to add another 13,400 positions annually through 2030.
The average master’s in psychology salary ultimately depends on geographical location and your particular concentration in psychology. Urban areas have higher pay and a more extensive client base, while less-populated areas of the country pay less.
Furthermore, the average starting salary for a master’s in psychology depends on where you live and work, your concentration in psychology, and the demand for people with your skills in psychology. For example, someone who lives in New Jersey and works as a clinical psychologist can expect to earn $106,160 as their average masters in psychology salary (labor statistics). In contrast, someone in West Virginia can expect a medical salary of about $60,000 with a master’s in psychology.
But, no matter where you live, earning a master’s in psychology will give you many options for a career. Or, it can be a stepping stone if you need a doctoral degree for your career goals!

Professional Organizations for Psychologists
Joining a professional psychologist organization allows you to access career and personal well-being support. Associations for psychologists are places where you can learn about the latest news in the field of psychology as well as your own, find resources for continuing education credits, look for jobs and get a feel for the current state of the psychology job market, and network with others who also work in your particular concentration.
Organizations also provide resources for self-care and what you can do to get relief when the work is draining. Some support psychologists from diverse backgrounds and provide support from a shared point of view.
American Psychological Association
The APA is the most well-known and respected association. It promotes psychological science advancement, communication, and application to benefit society and improve lives. The APA also offers the Psychology Student Network, a newsletter for students.
National Association of School Psychologists
The NASP represents over 25,000 school psychologists, graduate students, and related professionals in the nation and the world. The association’s mission is to ensure youth get the support they need for mental health, learning, and behavior to thrive in school.
American Counseling Association
The ACA has the vision to provide quality professional counseling to all who need mental health services to live a better life. The ACA promotes professional development, advocates for the counseling profession, and ensures ethical, culturally-inclusive practices for patients.
Mental Health America
MHA is a community-based nonprofit dedicated to helping those with mental illness and their needs and promoting overall mental wellness. The association promotes mental health and prevents mental illness through advocacy, research, and services in public and private mental institutions.
Association for Behavior Analysis International
The ABAI provides information and support for members interested in behavior analysis science, application, philosophy, and teaching. It sponsors events that focus on behavior analysis, provides continuing education opportunities, has job placement services, publishes scholarly journals, and supports the dissemination of behavioral analysis worldwide.
Your Career
Earning a master’s in psychology is a great option. Graduates gain access to a new career like a licensed marriage and family therapist. A master’s degree also prepares individuals to further their education with a doctoral degree.



Related:
- 15 Best Occupational Safety Bachelor’s Degrees
- Best Online Psychology Bachelor’s Programs
- Most Affordable Online Psychology Bachelor’s Degree Programs
- Best Medical Billing and Coding Degrees
- Best Online Counseling Master’s Programs
- 15 Best Online Psychology Master’s Programs
- Best Public Health Bachelor’s Degrees
- What Can You Do with a Human Service Degree?
- Best Types of Counseling Degrees